
 Prevent & Treat Insulin Resistance with Magnesium
Prevent & Treat Insulin Resistance with Magnesium
November is National Diabetes Month – did you know that research shows that optimal magnesium intake supports healthy blood glucose levels and prevents insulin resistance?
Magnesium (Mg) is a powerful mineral that is rarely consumed in adequate amounts. Mg is a cofactor or activator in hundreds of enzymatic reactions and required for numerous physiologic functions.1
Magnesium is involved in:
- RNA and DNA synthesis
- Protein, lipid, and carbohydrate metabolism
- Cell membrane stability maintenance
- Bone strengthening
- Vitamin D and calcium metabolism
- Nervous system function
- Immune activity
- Many more physiologic processes1,2
Magnesium also plays a predominant role in the production and utilization of energy in the body. Therefore, a magnesium insufficiency or deficiency can contribute to the development of an unhealthy metabolism, including abnormal blood glucose and insulin levels.1
 Magnesium and Metabolic Health (Metabolism)
Magnesium and Metabolic Health (Metabolism)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is cellular energy. Every molecule of ATP must bind to magnesium for conversion into the biologically active form – Magnesium-ATP (Mg-ATP) complex.3 In the mitochondria, where ATP is produced, the Mg-ATP complexes shuttle the ATP outside of the mitochondria so the ATP can be used as cellular energy.4
Magnesium supports mitochondrial function by increasing ATP production, decreasing the mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), boosting the activity of mitochondrial enzymes, reducing intracellular calcium overload, repolarizing the mitochondrial membranes, and minimizing overall oxidative stress.5
Continue reading below to learn more about the evidence-based beneficial effects of magnesium on healthy metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
 The Diagnosis of Magnesium Deficiency
The Diagnosis of Magnesium Deficiency
Magnesium must be consumed in adequate amounts daily to support optimal health. In the United States, the recommended daily allowance (RDA) for Mg is approximately 300-400 mg per day for adults. Ideally, adult females should consume 320 mg, and adult males should consume 420 mg of Mg per day. Unfortunately, epidemiological data show that the majority of those on a standard “Western diet” do not meet their daily Mg needs.1
Despite insufficient Mg intake by most individuals in the United States, magnesium deficiency is rarely diagnosed by physicians.1,2
Magnesium deficiency is challenging to diagnose because less than 1% of total body magnesium is in the blood; therefore, blood levels of Mg are not an ideal test to assess magnesium status.6 Diagnosing Mg deficiency is also difficult because the symptoms of Mg deficiency are non-specific and can mimic many other health conditions.7
Signs & Symptoms of Magnesium Deficiency & Insufficiency
Health concerns, symptoms, and signs associated with sub-optimal magnesium status may include:
- Abnormal bone metabolism
- Agitation
- Anxiety
- Asthma
- Back pain
- Cardiac arrhythmias
- Chronic fatigue syndrome
- Constipation
- Coronary spasm
- Decreased cardiac function
- Decreased glucose tolerance and altered glucose homeostasis
- Depression
- Digitalis sensitivity
- Headache
- Hearing issues
- Hyperactivity
- Hypertension
- Hypocalcemia
- Hypokalemia
- Impaired athletic performance
- Increased blood triglyceride and cholesterol levels
- Increased risk of metabolic syndrome
- Insomnia and other sleep disorders
- Insulin resistance
- Irritability
- Kidney stone recurrence
- Loss of appetite
- Low circulating levels of PTH
- Low circulating levels of vitamin D
- Low tolerance for stress
- Magnesium deficiency tetany
- Menstrual cramps
- Migraine
- Muscle spasms
- Nausea
- Neck pain
- Nervousness
- N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptors) more sensitive to excitatory neurotransmitters
- Nystagmus
- Osteoporosis
- Paresthesia (numbness and tingling)
- Poor memory
- Pregnancy complications, including miscarriage, premature labor, and eclampsia
- Resistance to parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Seizures
- Sodium retention8
- Thyroid dysfunction9
- Torsade de pointes
- Tremor
- Urinary spasms
- Vertigo
- Weakness8
 Low Magnesium Levels as a Cause of Disease
Low Magnesium Levels as a Cause of Disease
Therefore, if a patient has insomnia, anxiety, thyroid dysfunction, migraines, depression, high blood pressure, asthma, fatigue, insulin resistance, or any of the health concerns mentioned above, a magnesium deficiency could be the underlying cause of or a contributing factor to the health concern.
As you can see in the list of signs and symptoms above, adequate Mg intake is crucial for optimal blood glucose and insulin levels. The metabolic disorder known as insulin resistance is associated with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases, including heart failure and stroke.10,11,12
Magnesium supplementation in research settings appears to be beneficial for these diseases. A recent meta-analysis that included over one million participants from 40 clinical studies discovered that higher magnesium intake reduced the risk of stroke, heart failure, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality. According to the analysis, increasing the intake of Mg by 100mg per day reduced the risk of all-cause mortality by 10%, stroke by 7%, type 2 diabetes by 19%, and heart failure by 22%.13
 What is Insulin?
What is Insulin?
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the pancreas and is primarily known for its ability to lower blood glucose levels. Insulin was first discovered in 1921 by Frederick G. Banting and Charles H. Best in the laboratory of J.R. Macleod at the University of Toronto in Canada. Insulin is secreted from the β-cells of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans in response to the presence of glucose and amino acids in the blood after consuming food.14
As you can see in the picture below, insulin “unlocks” the glucose channel so blood glucose can enter the cell, where it will either be used as energy or stored as fat. As the glucose enters the cells due to the effects of insulin, the blood glucose level decreases.
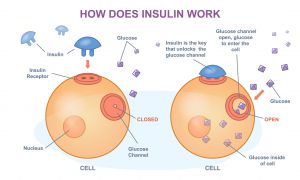 Insulin not only regulates glucose homeostasis (optimal blood sugar levels) but is also involved in tissue growth and development. Insulin exerts significant control over lipid metabolism (fat metabolism) because it stimulates lipid synthesis in the liver and adipocytes (fat cells). The presence of insulin also blocks the breakdown of adipose tissue (fat), which is known as lipolysis. Because insulin lowers the blood glucose level, it is administered as a medication to those with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and other health conditions.14,15
Insulin not only regulates glucose homeostasis (optimal blood sugar levels) but is also involved in tissue growth and development. Insulin exerts significant control over lipid metabolism (fat metabolism) because it stimulates lipid synthesis in the liver and adipocytes (fat cells). The presence of insulin also blocks the breakdown of adipose tissue (fat), which is known as lipolysis. Because insulin lowers the blood glucose level, it is administered as a medication to those with type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and other health conditions.14,15
When insulin levels are high (hyperinsulinemia) due to insulin resistance or an underlying genetic predisposition to releasing excessive insulin, it can exacerbate or be an underlying cause of many other health concerns, including obesity, diabetes, and cancer.16
 What is Insulin Resistance?
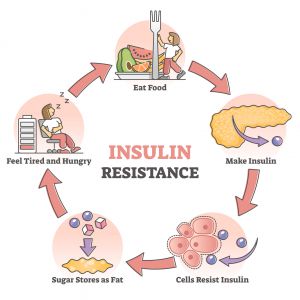
What is Insulin Resistance?
When considering the systemic effects of a hormone in the body, one must be mindful of the amount of hormone present AND the number and sensitivity of the hormone receptors. The hormone itself does not have any effect until it binds to a receptor.
Insulin resistance (IR) is a metabolic disorder characterized by high insulin levels due to the insulin receptors not responding optimally. This phenomenon could be caused by either a low number of receptors or receptors that do not appropriately respond to or are not sensitive to insulin.16,17
When the insulin receptors are resistant to the effects of insulin due to genetics or other factors, IR develops. The pancreas must produce extra insulin to force the blood sugar into the cells, resulting in an elevated blood insulin level, which is also known as hyperinsulinemia.17
There is controversy surrounding the development of IR since there are likely several underlying causes. Some believe IR develops, which then causes elevated insulin levels (hyperinsulinemia). In contrast, others suggest the pancreas produces extra insulin to compensate for elevated blood glucose levels, which then leads to IR. Then, some hypothesize both mechanisms occur in parallel to contribute to the development of IR. The relationship between hyperinsulinemia and IR is complicated and still being studied.18
 Magnesium & Insulin Resistance
Magnesium & Insulin Resistance
The relationship between magnesium and insulin resistance is fascinating and multifaceted. Low magnesium levels contribute to the development of both hyperinsulinemia and insulin resistance. Hyperinsulinemia increases the excretion of magnesium via the urine. Therefore, a low magnesium level could rapidly become critically low in the presence of excessive insulin.10
It is a vicious cycle that is similar to the magnesium/stress dynamic. As discussed in the article Synergistic Nutrients for Adrenal Support, stress hormones increase the amount of magnesium excreted in urine. Then, as magnesium levels decrease, the body’s resistance to stress wanes, which can then further increase the secretion of stress hormones, including cortisol, while exacerbating the magnitude of the magnesium deficiency.19
Optimal magnesium levels help protect against the development of insulin resistance via several mechanisms, which include:
- Reducing inflammation
- Normalizing cholesterol levels
- Improving glucose metabolism in the liver
- Optimizing calcium signaling
- Limiting the accumulation of adipose tissue (fat)
- Affecting the amount of insulin released
- Increasing glucose receptor gene expression1
- Supporting the activity of many Mg-ATP complex-dependent enzymes involved in glucose metabolism2
Regarding glucose receptor gene expression, the skeletal muscles take up approximately 80% of dietary glucose via the glucose receptors known as GLUT4 receptors. Several animal studies have shown that Mg supplementation increases GLUT4 gene expression, and one study was able to quantify the increased expression. Overall, Mg supplementation increases GLUT4 mRNA expression by approximately 23% to improve blood glucose management and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.5
 Results from the Canadian Health Measures Survey Cycle 3 (2012–2013) showed serum Mg levels in the Canadian population were negatively associated with body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose levels, fasting insulin levels, and HOMA-IR scores. The HOMA-IR test is the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance. HOMA-IR is calculated based on fasting plasma insulin and fasting plasma glucose levels. It is an objective measurement that assesses the severity of insulin resistance and the function of pancreatic β-cells.20
Results from the Canadian Health Measures Survey Cycle 3 (2012–2013) showed serum Mg levels in the Canadian population were negatively associated with body mass index (BMI), fasting blood glucose levels, fasting insulin levels, and HOMA-IR scores. The HOMA-IR test is the Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance. HOMA-IR is calculated based on fasting plasma insulin and fasting plasma glucose levels. It is an objective measurement that assesses the severity of insulin resistance and the function of pancreatic β-cells.20
So, the lower the blood magnesium level, the higher the insulin level and the HOMA IR score.20 Therefore, Mg deficiency may directly contribute to pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction.21
The results of at least five clinical trials verify that magnesium supplementation significantly reduces the fasting insulin level. When several clinical studies assessing the effect of magnesium supplementation on blood glucose and insulin levels are analyzed together, an increase of 50 mg of dietary magnesium daily leads to a 4.35% decrease in the HOMA-IR score and a 3.05% reduction in the fasting glucose level.22
 PCOS, Insulin Resistance, and Magnesium
PCOS, Insulin Resistance, and Magnesium
Patients with PCOS often present with irregular menstrual cycles, infertility, dyslipidemia, oligomenorrhea, metabolic dysfunction, insulin resistance, obesity, and symptoms of hyperandrogenism, such as acne, hair loss, hirsutism, anger, and irritability. PCOS is one of the most common endocrine disorders in female patients and the most common cause of anovulatory infertility.23
PCOS increases the risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and breast cancer. Therefore, treatment options are needed! Since there is a clear relationship between suboptimal magnesium status and insulin resistance, Shahmoradi et al. completed a triple-blind randomized controlled trial to determine if magnesium supplementation would alleviate the symptoms of PCOS.23
Participants with PCOS took 250 mg of magnesium oxide daily for two months. Patients were assessed before the magnesium intervention, after 2 months of supplementation, and again three months later (5 months after the initiation of the magnesium supplementation).23
The participants who supplemented with magnesium experienced a clinically significant reduction in mean serum insulin, mean HOMA-IR insulin resistance index, blood glucose, total cholesterol, and LDL levels. The participants who supplemented with magnesium also experienced a healthy increase in HDL levels. Participants who took the placebo did not experience improvements in metabolic parameters.23
 Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Insulin Resistance, and Magnesium Supplementation
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Insulin Resistance, and Magnesium Supplementation
Research suggests that Type 2 Diabetes and insulin resistance (IR) are more prevalent in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). RA is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that is characterized by synovial inflammation, leading to pain and stiffness in synovial joints.24
A recent prospective uncontrolled before-after study that included patients with RA discovered that six months of magnesium supplementation significantly reduced insulin, fasting blood glucose, and HOMA-IR (p<0.05). The dose of magnesium administered daily for six months was 300 mg.24
 Recommended Daily Dose of Magnesium for Optimal Insulin Levels
Recommended Daily Dose of Magnesium for Optimal Insulin Levels
You might be asking and pondering these questions:
- Which magnesium is best for insulin resistance?
- Should I prescribe magnesium to my patients with insulin resistance?
- What dose of magnesium is ideal for insulin resistance?
Unfortunately, we do not yet have answers to these questions, even though the results of many clinical trials and at least two systematic reviews do provide ample evidence of the benefits of magnesium supplementation on high insulin levels and blood glucose management in those who do not consume adequate Mg.22,25
Additional studies are necessary to determine the optimal dose, type, and timing of Mg supplementation to support healthy blood glucose and insulin levels in the future.22
Please note that too much magnesium can cause side effects, such as diarrhea. Consider prescribing a moderate-dose magnesium supplement that can be taken multiple times daily and offers high bioavailability to reduce the risk of side effects while optimizing magnesium levels and health benefits.

Saliva Insulin Tests Offer Functional Reference Ranges
The reference range used for fasting insulin levels in serum is controversial. Most laboratories suggest a serum fasting insulin level of less than 25 mIU/mL is “normal.” However, research shows that a fasting insulin level > 9.0 mIU/mL in the serum is associated with a diagnosis of prediabetes.26 The reference ranges for the DiagnosTechs saliva insulin tests are ideal for health optimization.
Screen for Insulin Resistance with a Saliva Insulin Test
DiagnosTechs offers two saliva insulin tests with clinically useful reference ranges to optimally screen for insulin resistance and other health concerns – fasting insulin (ISN1) & non-fasting insulin (ISN2). Ideally, patients will complete the Carbohydrate Stimulation Test by consuming a 75-gram of carbohydrate bolus one hour before collecting saliva in the NOON vial for the postprandial (non-fasting) insulin test to screen for insulin resistance. You and your patients may also choose to test the insulin response to any food or combination of foods.
Order functional salivary insulin testing with the following test panels:
The fasting (ISN1) & non-fasting (ISN2) saliva insulin tests can also be ordered as a two-test ISN Panel or as single tests.
To place a test order, click here. DiagnosTechs will drop ship test kits directly to your patient’s home. Select this option at the top of the order form.
Please visit our Provider Tools page for more information about Insulin Resistance and Blood Sugar Dysregulation and choosing the right test panel.
 References:
References:
- Pelczyńska M, Moszak M, Bogdański P. The Role of Magnesium in the Pathogenesis of Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients. 2022;14(9):1714. doi:10.3390/nu14091714
- Piuri G, Zocchi M, Della Porta M, et al. Magnesium in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. 2021;13(2):320 doi:10.3390/nu13020320
- Beard DA, Marzban B, Li OY, et al. Reduced cardiac muscle power with low ATP simulating heart failure. Biophys J. 2022;121(17):3213-3223. doi:10.1016/j.bpj.2022.07.029
- Firetag LE. Upgrade your energy this summer! InterPlexus. Published July 8, 2022. Accessed January 11, 2023.
- Hosseini Dastgerdi A, Ghanbari Rad M, Soltani N. The Therapeutic Effects of Magnesium in Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance. Adv Biomed Res. 2022;11:54. doi:10.4103/abr.abr_366_21
- Ahmed F, Mohammed A. Magnesium: The Forgotten Electrolyte-A Review on Hypomagnesemia. Med Sci (Basel). 2019;7(4):56. doi:10.3390/medsci7040056
- Razzaque MS. Magnesium: Are We Consuming Enough?. Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1863. doi:10.3390/nu10121863
- Gröber U, Werner T, Vormann J, et al. Myth or Reality-Transdermal Magnesium?. Nutrients. 2017;9(8):813. doi:10.3390/nu9080813
- de Sousa Melo SR, Dos Santos LR, da Cunha Soares T, et al. Participation of Magnesium in the Secretion and Signaling Pathways of Insulin: an Updated Review. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2022;200(8):3545-3553. doi:10.1007/s12011-021-02966-x
- Gommers LM, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ, et al. Hypomagnesemia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Vicious Circle?. Diabetes. 2016;65(1):3-13. doi:10.2337/db15-1028
- Deng XL, Liu Z, Wang C, et al. Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke. Metab Brain Dis. 2017;32(5):1323-1334. doi:10.1007/s11011-017-0050-0
- Jia G, Whaley-Connell A, Sowers JR. Diabetic cardiomyopathy: a hyperglycaemia- and insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 2018;61(1):21-28. doi:10.1007/s00125-017-4390-4
- Fang X, Wang K, Han D, et al. Dietary magnesium intake and the risk of cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and all-cause mortality: a dose-response meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. BMC Med. 2016;14(1):210. doi:10.1186/s12916-016-0742-z
- Roberts CK, Hevener AL, Barnard RJ. Metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: underlying causes and modification by exercise training. Compr Physiol. 2013;3(1):1-58. doi:10.1002/cphy.c110062
- van Niekerk G, Christowitz C, Conradie D, et al. Insulin as an immunomodulatory hormone. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2020;52:34-44. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.11.006
- Zhang AMY, Wellberg EA, Kopp JL, et al. Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer [published correction appears in Diabetes Metab J. 2021 Jul;45(4):622]. Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):285-311. doi:10.4093/dmj.2020.0250
- Kasuga M. Structure and function of the insulin receptor-a personal perspective. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2019;95(10):581-589. doi:10.2183/pjab.95.039
- Hall C, Yu H, Choi E. Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med. 2020;52(6):911-920. doi:10.1038/s12276-020-0456-3
- Firetag L. Synergistic nutrients for adrenal support – part 2. InterPlexus. Published December 5, 2022. Accessed January 20, 2023.
- Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(6):1487-1495. doi:10.2337/diacare.27.6.1487
- Kostov K. Effects of Magnesium Deficiency on Mechanisms of Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes: Focusing on the Processes of Insulin Secretion and Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1351. doi:10.3390/ijms20061351
- Morais JBS, Severo JS, de Alencar GRR, et al. Effect of magnesium supplementation on insulin resistance in humans: A systematic review. Nutrition. 2017;38:54-60. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2017.01.009
- Shahmoradi S, Chiti H, Tavakolizadeh M, et al. The Effect of Magnesium Supplementation on Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Profiles in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: a Randomized Clinical Trial [published correction appears in Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024 May;202(5):2402. doi: 10.1007/s12011-023-03794-x.]. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2024;202(3):941-946. doi:10.1007/s12011-023-03744-7
- Norouzi M, Rezvankhah B, Haeri MR, et al. Magnesium supplementation and insulin resistance in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Transl Myol. 2022;32(3):10622. doi:10.4081/ejtm.2022.10622
- Simental-Mendía LE, Sahebkar A, Rodríguez-Morán M, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on the effects of magnesium supplementation on insulin sensitivity and glucose control. Pharmacol Res. 2016;111:272-282. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.06.019
- Johnson JL, Duick DS, Chui MA, Aldasouqi SA. Identifying prediabetes using fasting insulin levels. Endocr Pract. 2010;16(1):47-52. doi:10.4158/EP09031.OR


